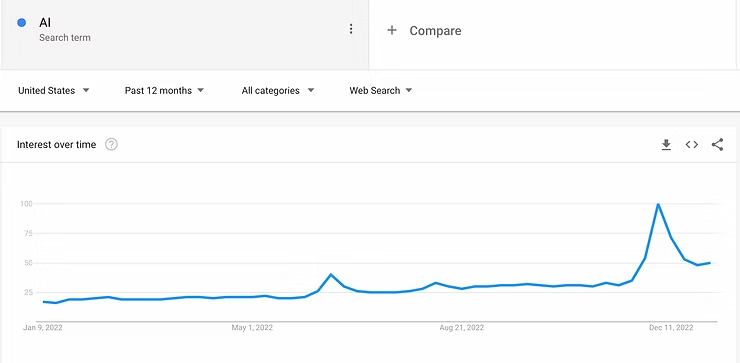
Generative AI systems like ChatGPT, recently made available by OpenAI, are a fascinating use of emerging technology that has captured the world’s attention. Search instances for “AI” peaked at an all-time high in December 2022 as a direct result of conversations about that system (trends.google.com). It’s not just the “tech nerds” that know about this stuff now and to say many in the education industry are “worried” is a colossal understatement (e.g., Downs, 2023; Warner, 2022). These systems hold a lot of promise for how they will positively impact our lives. Still, they challenge our notions of intellectual property and who is rightfully the owner or creator of a piece of art, a written passage, or an idea. Certainly, those of us in the education industry will need to wrestle with whether using these tools is “cheating”, if students should be allowed to use them, or under what circumstances it is acceptable.
A difficult aspect of determining whether it should be considered cheating is what acceptable help is. For example, Grammarly is an AI-powered tool to improve writing. It doesn’t usually generate long passages, but it effectively suggests changes. It can be a powerful tool for allowing students who are not native speakers to participate more completely in their education, but the applications for Grammarly are broader than that. Most of our company uses a Grammarly license, including very competent writers. I’m using it now because it helps me ensure a better final product with less effort. Helping people do a better job more quickly is what good tools are for.
Using Grammarly to write this piece does not feel ethically questionable. Hopefully, no one thinks I am dishonest or a cheater. But what if I were using Grammarly on a graded university paper? Probably still ok to most, akin to using spell check. Yet if I used ChatGPT to generate a university paper I suspect the feeling would be different. Why? The amount of help might be different, but not the kind of help. With both technologies, I would benefit from writing generated for me, not by me. Both tools would allow me to produce more and better writing faster than I otherwise could.
There are obviously many ethical considerations here, not the least of which concerns equitable access to the same tools (e.g., Grammarly has more advanced tools for paying customers). Yet, regardless of our feelings, the number and sophistication of these tools is growing. As Grammarly illustrates, they are already an integral part of the 21st-century work world. The people and companies that leverage them will gain a competitive advantage, which is the same reason students are using them and we are worried about them. The horse is already out of the barn. Realistically, this horse broke through the barn doors, leaped the pasture fence, and doesn’t care what the farmer thinks.
Finding the Horse and Forcing it Back
When considering our best courses of action, one strategy is to essentially fight the use of AI. We can attempt to detect the use of these tools and to “dissuade” students from using them by penalizing their grades. I will call this the “detect and punish” approach and some instructors and tools are trying to detect and flag AI-generated writing. Many ed-tech products also use this approach for plagiarism, integrating technologies like Turn It In for detecting plagiarized content. Like AI-assisted writing, students often plagiarize to finish assigned writing tasks more quickly or get a better grade. Therefore, while plagiarizing may appear different than using AI assistance, the student motivations to do it and approaches for addressing it are typically similar. While the “detect and punish” strategy may tamp down these problems because of the fear of getting caught, the strategy does not address why students are motivated to cheat.
Among the former college instructors that make up our success team here at Yellowdig, we largely agreed that cheating tends to happen when stakes are high for failure or students do not value an assignment. Both of these causes can be addressed by altering course designs. For example, you can gamify course elements to remove the notion of permanent failure and to give students a little more choice about where and when to participate. If the stakes are not high for failure or missing a deadline, students are less likely to risk cheating, and instructors are more likely to be able to foster a growth mindset toward improving (“If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again”).
Significantly fewer students will risk cheating on an assignment if they enjoy doing it, believe it is helping, and they do not face a permanent hit to their grade for any misstep. Research by Blackwell et al., (2007) found that a growth mindset was related to positive learning strategies, like students saying “I would work harder in this class from now on” or “I would spend more time studying for tests”. Those who failed and had a more fixed mindset were more apt to say things like, “I would try not to take this subject ever again,” “I would spend less time on this subject from now on,” or “I would try to cheat on the next test.” The use of AI or plagiarism to quickly complete an assignment is the embodiment of these “negative strategies.” The study also found that growth mindset, learning goals, positive beliefs about effort, non-helpless attributions, and strategies in response to failure are all interrelated. That means if we are able to foster a growth mindset and a focus on improvement, students are less likely to use “negative strategies” (i.e., cheating and avoidance).
Ultimately, though, the problem with the “detect and punish” approach is that it creates an “arms race” with a predictable outcome; without addressing why students are motivated to cheat, students simply find increasingly sophisticated, undetectable ways to cheat. As AI tools get better at creating novel things that are indistinguishable from human-generated works, any AI detectors will increasingly fail to differentiate them. Similar things are already happening with students learning to “game” plagiarism detectors by editing plagiarized passages and running them through plagiarism detectors until they fail to trigger. As fast as we might try to improve the detection of cheating, students will use the same tools to defy detection. Students that do these kinds of things to avoid detection are still doing the bad thing we wish they would avoid (e.g., stealing intellectual property), but they are simply making it so that we don’t realize they are. This outcome is not a “win.”
Sophisticated deception is an intractable problem for the “detect and punish” approach. While the approach can help instructors address cheating by detecting truly AI-generated or truly plagiarized content (i.e., true positives), neither instructors nor the AI detector tools can possibly know how many false negatives there are and how many students are cheating undetected. As computers increasingly approach the ability to pass the Turing Test and become better at mimicking human writing and art, the number of false negatives for the detection approach will climb. If we are not already there, soon enough there will be no reliable technological or human method of detecting students’ use of AI. At Yellowdig, we have certainly created ways to assist instructors in identifying students who are participating poorly or not participating at all. And we will continue to consider smart features to help with that. However, we mostly view the “detect and punish” approach as a dead-end road in addressing these threats. Similarly, we believe most attempts to “fight” the proliferation of students using AI assistance are doomed to failure. In short, we can spend a lot of time finding and trying to lasso this horse to get it back to the barn, but the odds are we’re going to spend a lot of time and effort and still get kicked by it.
Luring the Horse Back
Many educators will be discussing how to address AI in education in the coming months, particularly for writing assignments and short-answer or essay-based assessments. Warner (2022) offers some concrete recommendations now, in what appears to be a planned series on the topic. Most of their advice, and indeed much of our thinking, can be summed up with this quote from that article: “I still believe students want to learn, but this means giving them something worth doing.” If we want to get this horse back into the pasture and possibly back into the barn, it has to go there voluntarily. We have to focus on propelling deeper and higher-order learning and change the way we think about assessment so that students focus on what truly matters.

At Yellowdig, our main approach to addressing these concerns is, and always has been, to increase student motivation to participate thoughtfully. Our system and the community-focused pedagogy it supports aim to provide an experience where there is far more motivation to learn and thoughtfully participate than to cheat. Yellowdig communities are not places where students go to respond to an assignment, create content before a deadline, leave, and get graded on it. Yellowdig communities, instead, become a constant source of helpful information and support via interactions with others. This helps drive deeper learning that students value. Yellowdig uses grades as part of its system, but assessing students is not the end goal. The purpose of the gameful learning point system is to create behavioral change in students that leads to the formation of a valuable digital space. Once that space forms, participation becomes intrinsically motivating for students. Students are visiting their communities because they can get information and have conversations that will help them learn more and succeed in their classes, not because they might lose part of their grade.
When students are experiencing that kind of environment, they typically want to participate and voluntarily do much more than is required. The reality is that there is no need or desire to “cheat” to get full marks if you value doing something, do not consider it “busywork,” and can see pathways for getting full marks without cheating. Our system and pedagogical approach enable this:
Most students voluntarily visit and participate in open communities that provide valuable information and opportunities to interact. When motivation is high, cheating to be done with the assignment quickly will be low.
When students interact with real people in a conversation, they know other people are paying attention. When students know that others are reading what they produce, they are more motivated to produce better content and less likely to think they can “get away with” poor content or cheating.
The context of a real conversation makes it difficult to copy passages or generate AI responses that fit the context. Because conversations have to be responsive to others, it is difficult to plagiarize or generate AI content that “fits” a conversation.
In real conversations, students don’t respond to others who post out-of-context or low-quality material. If a student regularly generates social interactions that are “off the mark,” other students’ interactions with them typically reveal it. Our point system uses student behavior to reward students who are adding positively to conversations, but that same data is useful for noticing poor participation.
Students that build real relationships with instructors and peers feel more social responsibility to thoughtfully participate. There are more risks associated with cheating or “phoning it in” when real relationships have formed. Cheating students do not just risk their grade; they risk being ostracized. The social contracts that emerge among members of a healthy community have powerful positive impacts on motivation, lead to more collaboration and cooperation, and dissuade many forms of poor participation.
Pedagogy matters, and if your community asks students to generate responses to prompts or has regular deadlines, students will have more motivation and ability to cheat. Specific concerns about this approach related to assistive technology are:
A prompt can be pasted into a search engine or AI generator to find an accurate response that can be copied, making cheating simple.
Hard deadlines increase cheating. Rather than permanently lose points missing a deadline, a guaranteed bad outcome, students may cheat and hope to get away with it. Yellowdig’s point system and pedagogy suggestions enable enough flexibility and agency that there are no hard deadlines, few ways to lose points permanently, and many pathways to contributing to the community while receiving full marks. These design advantages for Yellowdig, which are also important for student equity considerations, are negated when instructors add hard deadlines.

Designing the situation to reduce cheating to the point that it is no longer a serious concern is important and does work. It will also tend to have positive side effects that increase the quality of most student participation. Beyond that we strongly believe that setting expectations from the outset and having conversations about the use of AI and plagiarism are the most promising and transformative ways to address these technologies. Getting the horse back in the barn does not require finding it or wrangling it. We have to make the barn a place the horse wants to be.
Allowing the Horse Some Space to Roam
The reality, as mentioned earlier, is that generative AI and other machine-learning assistive technologies are already a fixture of the modern workplace. There are both appropriate applications for nearly all of these technologies and legal and ethical concerns. While we could take a prohibition-style approach to using assistive technologies, simply prohibiting students from using these technologies will only lead to them having a poor understanding of the opportunities and threats they present. Besides, what is the point of having a horse if you can’t take it out of the barn?
Students must learn to use intellectual property ethically, cite their sources, and disclose their methods for producing a piece of work. They must also learn to express their own thoughts coherently in many situations. These are all important skills for them to master before graduating. Importantly, as new technologies emerge and new situations arise throughout their lives, they will need to be able to apply those skills flexibly and in novel situations. Considering how we want students to behave beyond our class, we should probably not be preventing the use of these technologies. Rather, we must prepare learners to make ethically appropriate decisions about the content they create and the sources they use.
A Yellowdig community is a great place to have conversations about these topics with your students. Most importantly, once you have open conversations about these issues, it creates a safe space for them to ask additional questions, to clarify your expectations further, or to be able to address these topics in new situations as they arise. Rather than viewing these tools as a threat to intellectual honesty and education at large, we must use them as opportunities to discuss the nuanced issues of the appropriate use of AI tools and use those conversations to build a stronger and more informed intellectual community. As educators, it feels like our best way to deal with this horse is to plan when, why, and how we allow it some freedom to stretch its legs.
References
Blackwell, L. S., Trzesniewski, K. H., & Dweck, C. S. (2007). Implicit Theories of Intelligence Predict Achievement Across an Adolescent Transition: A Longitudinal Study and an Intervention. Child Development, 78(1), 246–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2007.00995.x


